Cloudbursts: Understanding Extreme Rainfall Events
Exploring the Causes, Impacts, and Challenges of Predicting Devastating Localized Downpours in India.
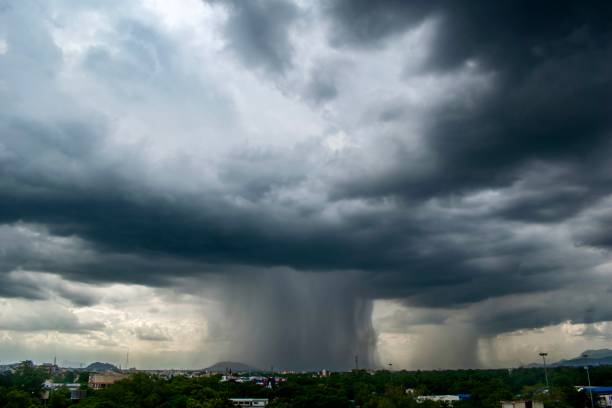

A cloudburst is an extreme weather event characterized by a sudden, very heavy downpour of rain over a small geographical area and for a short duration. While the term might evoke an image of a cloud "bursting," it's a meteorological phenomenon resulting from specific atmospheric conditions.
Here's a breakdown of what a cloudburst entails:
1. Definition:
- The India Meteorological Department (IMD) defines a cloudburst as rainfall exceeding 100 mm (10 cm) per hour over an area of approximately 20-30 square kilometers.
- Some definitions also consider 5 cm of rain in 30 minutes over the same area as a cloudburst.
- It's often accompanied by hail and thunder.

2. How Cloudbursts Form:
- Cumulonimbus Clouds: Cloudbursts are typically associated with cumulonimbus clouds, which are large, vertically developed clouds capable of holding immense amounts of moisture.
- Rapid Updrafts: Warm, moist air rises rapidly from the ground, carrying water vapor upwards. These strong upward air currents (updrafts) prevent the condensing raindrops from falling to the ground.
- Accumulation of Water: A large amount of water accumulates at high altitudes within the cloud.
- Sudden Release: If these upward currents suddenly weaken or cease, the accumulated water descends rapidly and forcefully over a small area, leading to the "burst" of rain.
- Orographic Lifting: In mountainous regions, this process is intensified. When moist air encounters a mountain, it is forced to rise (orographic lifting). As it rises, it cools and condenses rapidly, leading to the formation of dense clouds and intense precipitation, making hilly areas particularly prone to cloudbursts.
- Atmospheric Instability: Significant temperature differences between upper and lower atmospheric layers can cause rapid convection and intense rainfall.
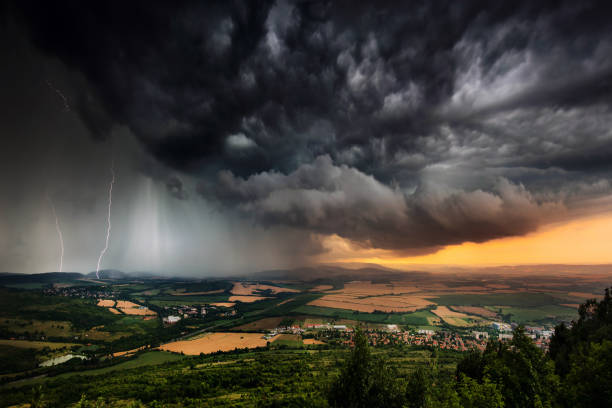

3. Impact and Consequences:
Cloudbursts have devastating impacts due to the sheer volume of water released in a short time:
- Flash Floods: This is the most immediate and dangerous consequence. The sudden influx of water overwhelms natural drainage systems, causing rapid and severe flooding, especially in low-lying areas and riverbeds.
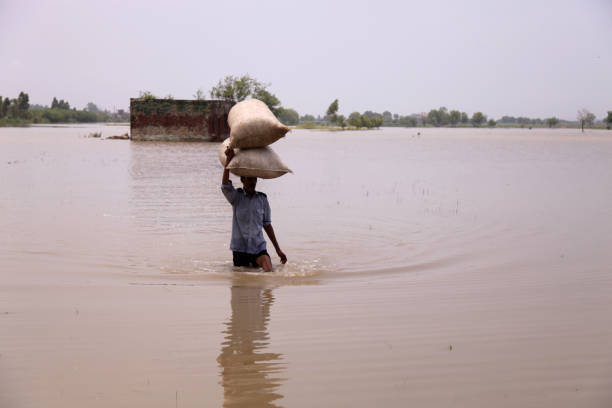

- Landslides and Mudflows: The intense rainfall saturates the soil on slopes, reducing its stability and triggering landslides and mudflows, which can sweep away homes, roads, and infrastructure.

- Loss of Life and Property: Cloudbursts frequently result in significant loss of human and animal lives, destruction of houses, buildings, bridges, roads, and agricultural land.

- Disruption of Infrastructure: Transportation networks (roads, bridges), communication lines, and power supply systems are often severely disrupted.
- Environmental Damage: Forests, crops, and ecological balance can be severely impacted.
4. Challenges in Prediction:
- Cloudbursts are extremely difficult to predict accurately due to their localized nature and sudden occurrence.
- Current satellite and radar technologies, while good for larger weather systems, often lack the resolution to detect and forecast these small-scale, intense events with sufficient lead time.
5. Recent Cloudburst Events in India:
India, particularly its Himalayan regions and the Western Ghats, is highly susceptible to cloudbursts during the monsoon season. There have been numerous incidents in recent years:
- April-May 2025: Several reports of cloudbursts in Himachal Pradesh (Rampur, Kullu), Jammu & Kashmir (Ramban, Kupwara), and Sikkim leading to flash floods and landslides, causing casualties and significant damage.
- Monsoon 2024: Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand, and Jammu & Kashmir witnessed numerous cloudburst incidents leading to fatalities and widespread damage to infrastructure and property. For example, Himachal Pradesh reported 51 cloudburst and flash flood events between June 27 and August 16, 2024, resulting in 31 deaths.
- Monsoon 2023: Continued reports of cloudbursts across the Himalayan states and parts of North East India.
- Previous Years (e.g., 2022, 2021, 2013 Kedarnath): India has a history of catastrophic cloudburst events, particularly in mountainous regions like Uttarakhand, Himachal Pradesh, and Jammu & Kashmir, and even in urban centers like Mumbai (2005).
Understanding cloudbursts is crucial for disaster management and mitigation efforts, especially in vulnerable regions. This includes developing better early warning systems, promoting sustainable land use, reforestation, and resilient infrastructure.