Diverse Biodiversity Hotspots of India: A Tapestry of Natural Beauty and Rarity
India's top biodiversity hotspots: Western Ghats, Eastern Himalayas, Sundarbans, Arunachal Pradesh, Indo-Burma, Andaman-Nicobar, Central Western Ghats. Conservation vital amid threats.
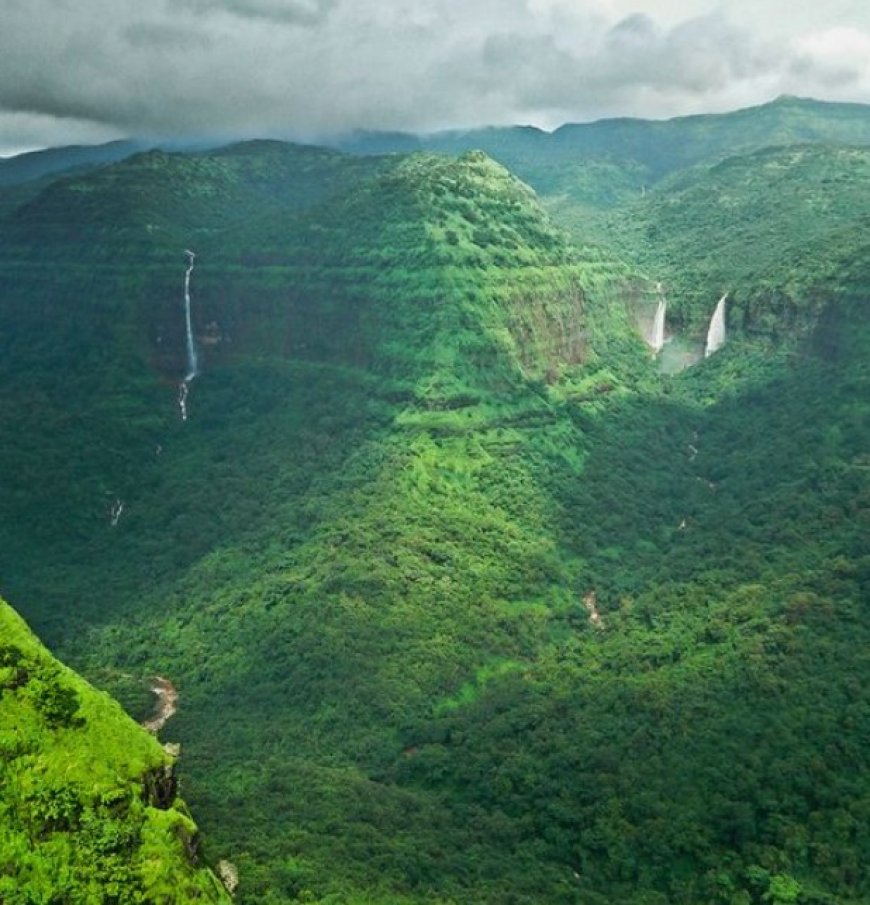

India is a biodiversity hotspot, famous for allure marvellous environmental sort. Seven of allure most remarkable biodiversity hotspots involve:
1. Western Ghats: This UNESCO World Heritage Site is a biodiversity cache, protecting a various range of vegetation and animal world, many of that are native. The domain is home to variety like the Malabar giant hoard, feline-tailed macaque, and numerous native toads.
2. Eastern Himalayas: Stretching across India's northeastern states, this domain boasts a singular join of lush, subtropical, and mountaintop environments. Species like the flaming panda, snowstorm cheetah, and Assam cover turtle find church in this place.

3. Sundarbans: This mangrove environment spans across India and Bangladesh, providing residence for the impressive Royal Bengal cougar, sea attacker, and a myriad of chum and fowl class.

4. Western Arunachal Pradesh : Part of the Eastern Himalayas, this area shelters various vegetation and animal world, containing the Arunachal macaque, Himalayan evil bring, and many class of orchids.

5. Indo-Burma Region : Encompassing parts of northeastern India, this hotspot boasts extreme levels of endemism, accompanying variety like the Hoolock ape, Blyth's tragopan, and the Manipur shrub-quail.

6. Andaman and Nicobar Islands : These detached enclaves harbor wonderful biodiversity, containing the Nicobar megapode, Andaman intense boar, and a range of singular pink class.

7. Central Western Ghats : This substitute-domain inside the Western Ghats is home to the Nilgiri tahr, great Indian hornbill, and a money of salamanders, making it a important district for preservation.

India's rich biodiversity faces many dangers, containing residence deficit, mood change, and trespassing. Conservation efforts are owned by continue these unable to be fixed environments and the variety they support.