Maintaining Calcium Balance: Achieving Healthy Calcium Levels for Optimal Health
A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Calcium, Its Role in the Body, and Strategies for Effective Management
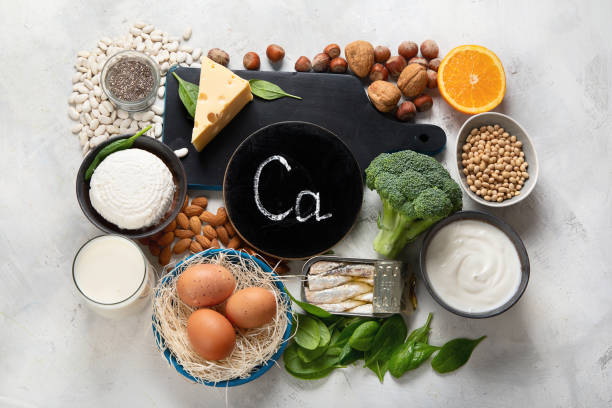

Yes, here's a blog post explaining how to manage your calcium intake:
Retaining Calcium Equilibrium: A Handbook for Reaching Adequate Calcium Levels
Calcium is an essential mineral that is necessary for many body processes, such as blood coagulation, nerve communication, muscle contraction, bone health, and hormone control. For general health and wellbeing, it is important to maintain optimum calcium levels.
Imbalances in Calcium

Numerous health issues can result from excessively high (hypercalcemia) or too low (hypocalcemia) calcium levels.
Symptoms of Hypocalcemia
* Tetany (muscle stiffness), cramps, or spasms in the muscles
* Hand, foot, and facial numbness and tingling
* Convulsions
* An irregular pulse
* Osteoporosis, or brittle bones
Symptoms of Hypercalcemia
* Increased urination and thirst
* Exhaustion
* Experiencing nausea and vomiting
* Indigestion
* Pain in the bones
* Kidney stones
Influential Factors on Calcium Levels
Calcium levels can be influenced by a number of circumstances, including:
Dietary intake: To maintain calcium levels, eat foods high in calcium, such as dairy products, leafy green vegetables, and fortified meals.
DHA: Calcium absorption from the stomach is aided by vitamin D. Adequate levels of vitamin D can be ensured by sunlight exposure and supplementation with vitamin D.
PTH (parathyroid hormone): PTH controls blood calcium levels. Disorders of the parathyroid gland can throw off the calcium balance.
Specific drugs: Certain drugs, such steroids and diuretics, can alter calcium levels.
Methods for Preserving Calcium Levels
Nutritional Calcium
* Eat foods high in calcium, such as tofu, leafy greens (broccoli, kale, collard greens), dairy products (milk, cheese, yogurt), and fortified foods (cereals, orange juice).
Calcium D
* Make frequent exposure to the sun.
* If you don't get much sun exposure, think about taking vitamin D pills.
Changes in Lifestyle
* Frequent exercise improves calcium absorption and bone health.
* Steer clear of alcohol intake that is too high since this may disrupt the metabolism of calcium.
* Give up smoking, as it can lead to calcium imbalances and bone loss.
Medical Supervision
Medical intervention may be required in certain instances to control calcium levels. This can involve taking vitamin D or calcium supplements, or using drugs to control PTH levels.
Keeping an Eye on Calcium Levels
Frequent blood tests can assist in tracking calcium levels and early detection of any abnormalities.
Talking with a Medical Expert

Seek individualised advice and support from a healthcare expert if you are concerned about your calcium levels. They are able to evaluate your risk factors, propose suitable testing, and offer practical management advice.
Keeping calcium levels in check is essential for general health and wellbeing. You may successfully control your calcium levels and protect your long-term health by including foods high in calcium into your diet, making sure you get enough vitamin D, adopting healthy lifestyle practices, and getting medical guidance when needed.
Never forget that health is riches. Invest sensibly in it.