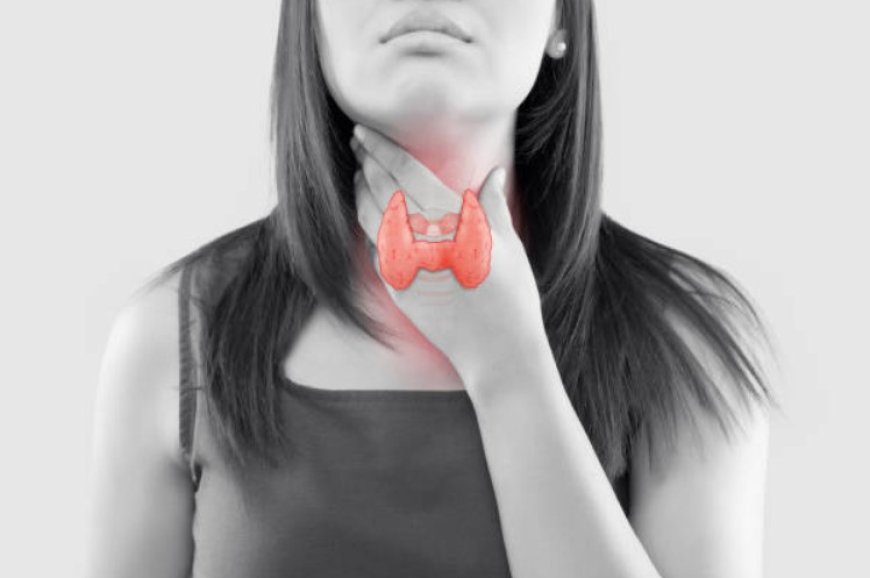
What causes thyroid disorders?
Understanding the root causes of thyroid problems
What causes thyroid conditions?
A little gland in the neck called the thyroid makes hormones that control metabolism. When the thyroid gland produces these hormones either too much or too little, thyroid problems can result.
Thyroid diseases can be brought on by a variety of factors, including:
Autoimmune conditions: The immune system of the body targets healthy tissues in autoimmune disorders. The most frequent autoimmune cause of hypothyroidism is Hashimoto's thyroiditis, and the most frequent autoimmune cause of hyperthyroidism is Graves' disease.
Insufficient iodine: The mineral iodine is necessary for the synthesis of thyroid hormones. Hypothyroidism can result from iodine shortage, particularly in pregnant women and young children.
Prescription drugs: The thyroid gland may be affected by specific drugs. Lithium, for instance, which is prescribed for bipolar disorder, can result in hypothyroidism.
Radiation treatment (RT) The thyroid gland can be harmed by radiation therapy to the head or neck, which can result in hypothyroidism.
Thyroiditis An inflammation of the thyroid gland is known as thyroiditis. An autoimmune response, a virus, or a bacterial infection can all lead to thyroiditis.
Nodules on the thyroid Nodules in the thyroid gland are lumps or growths. The majority of thyroid nodules are benign, however some can overproduce thyroid hormone.
Disorders of the pituitary gland: A little gland at the base of the brain called the pituitary gland makes hormones that regulate other glands, including the thyroid gland. Thyroid hormone production may be impacted by pituitary disorders.
Genetics: Some thyroid conditions are inherited. For instance, those with a family history of the ailment are more likely to develop Hashimoto's thyroiditis.
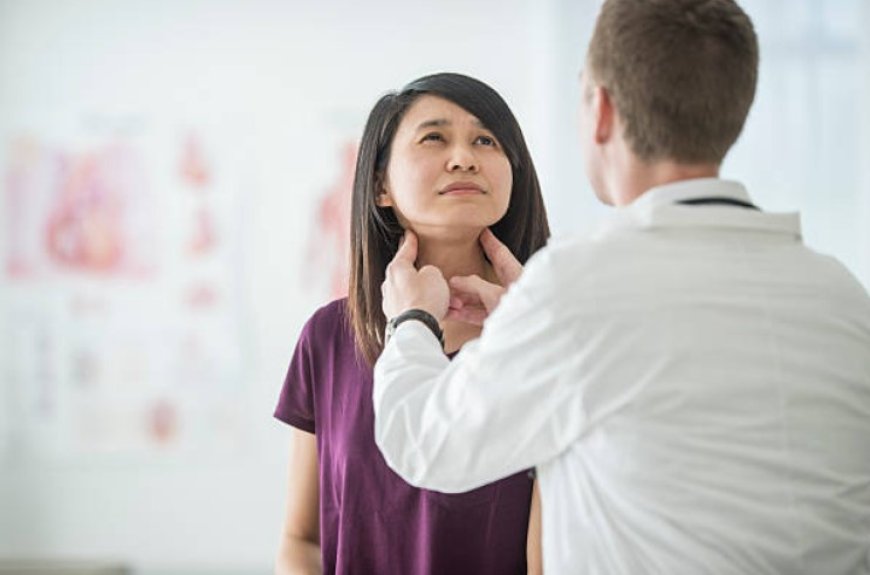
It's crucial to visit a doctor if you have thyroid health concerns. To find out if you have a thyroid disorder, a doctor can run testing and make treatment recommendations.
Thyroid disorder treatment
The cause of the condition and the intensity of the symptoms affect the treatment for thyroid disorders. Options for treatment include:
Medication: Hypothyroidism may be treated with thyroid hormone replacement therapy. In patients with hyperthyroidism, medications may also be utilized to prevent the thyroid hormones from being produced.
Iodine radioactively present: When a person has hyperthyroidism, thyroid tissue can be removed using radioactive iodine.
Surgery: When a person has a large goiter or thyroid cancer, surgery may be required to remove all or a portion of the thyroid gland.
It's crucial to collaborate with your doctor to create a treatment strategy that is appropriate for you if you have a thyroid condition.